How to Use Gamification in Healthcare Mobile Apps to Improve Users’ Health?
Gamification is probably something you have heard about in various industries or cases. This is an example of gamification if you play a mobile application and take action towards a certain goal.
As a concept, collecting points, coins, and awards for fulfilling a set of activities has been around for a while, but it’s gaining popularity in more niche industries these days.
Its importance, role, and examples of how it’s used in healthcare mobile apps will be discussed today. What is the relationship between healthcare, mobile apps, and gamification? The mix turned out to be quite successful.
What is Gamification and Why Does It Matter?
In a nutshell, gamification involves using game elements and game design techniques outside of a traditional gaming context. It is meant to engage people, motivate them, and stimulate them to act while attaining the desired behavior or other goals.
While this is nothing new to games or many mobile apps (complete all tasks to earn rewards), it is still relatively new to the world of healthcare mobile apps.
What are the reasons for the increased use of gamification in business?
Apps rich in gamification force time and loyalty commitments. Gamification stimulates a range of processes and behaviors, but they all lead to increased app engagement and usage.
Users may choose to be motivated by the feeling of community and socializing, while others may be motivated by receiving rewards for specific accomplishments, competing against others, viewing data and measurements regarding small achievements, or finding enjoyment in the entire process. Either way, gamification makes users not only download the app or use it once – it makes them hooked to their screens, which automatically translates to higher revenue. The raw data alone is not enough to motivate people these days, they need challenges, rewards, or some sense of community and gamification is the ticket.
Gamification encourages users to be curious, which motivates them to keep playing and earn rewards. Moreover, gamification allows for competition – Displaying players’ achievements on the scoreboard encourages them to keep striving for more and compare themselves to others. As no one likes to be forced into doing something, gamification gives users control by allowing them to decide what milestones to complete next.
Many of these factors are combined in technology, making it a resource-freeing tool that contributes towards achieving desired goals.
What Are the Best Ways to Build a Gamified App?
There are a number of gamification features and options you can incorporate into a mobile app, and the possibilities are rather limitless. You can implement them separately, but combining them may be most effective.
- Daily log-in – users are rewarded for everyday log-in to the app. This may be a reward in the form of extra in-app currency or boosters to use in-app but may make people stick to your app for longer to actually use it. Often, users get unlimited lives when they complete a few daily log-ins (e.g. 15 minutes). This forces users to make the most of it and stay in the app for long periods of time.
- Progress bars – once progressing with some levels, the progress bar may grow and lead to some rewards on the way (e.g. on the 30% or 60% level).
- Badges – there may be a couple of badges waiting for the users to complete some levels, get to some achievements, or upon other actions (e.g. recharging energy with a purchase of coins).
- Quests and time-bound events – if a particular user completes a quest or a special time-bound event, they may be rewarded in the end – that keeps users motivated to complete the event.
- In-app currency (diamonds, coins) – in-app currency such as diamonds or coins can be then exchanged for goods or tools inside the app or help overcome obstacles or blockades of the next level.
- Scoreboards – users can compare their performance with other users and see how they rank in particular categories.
- Leagues – joining the leagues and competing towards a common goal (e.g., first place in regatta) or team prizes.
- Karma/strike – once a user gets to a particular level of karma/strike (e.g. by performing a few actions in a row) they can unlock new items, levels, and other perks.
- Social media shares – a particular user can share their achievements on social media and reach brand new users or simply emphasize their loyalty to an app.
- Free incentives – if a particular user hasn’t logged in to an app for a while, a new log-in can grant them extra perks.
- Referrals – referring users to the app can result in getting extra perks (e.g. lives).
- Stars – users can receive a range of stars that reflect their progress (and they may want to beat the level again to get more stars).
All these mechanisms contribute to the feeling of rivalry within the community and complement one another. What are the benefits of it for businesses? Gamification and freemium apps work together to build and maintain user loyalty and increase the chances of more users making purchases in the app.
People will even pay more when stuck in one level, as it’s a hindrance to their „joy”. The only way to get around such a stumbling block is to buy extra features, coins, or tools to use in the app and „unblock” their fun.
Are you wondering how it can work with healthcare apps? Wonder no more, as we’re providing you with examples in the next paragraphs.
What Are the Benefits of Mobile Apps for the Healthcare Industry?
In the past, the only way patients communicated with doctors was through direct appointments. The health of patients could not be continuously monitored by doctors or hospitals, and therefore sharing real-time recommendations was not possible.
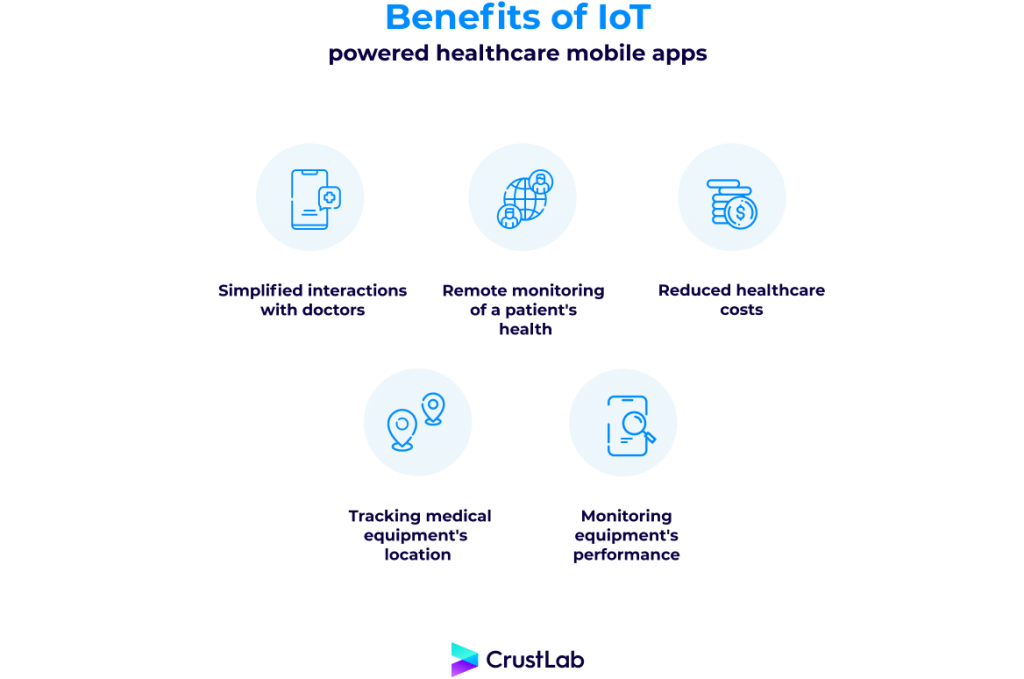
With IoT, they can. What are the benefits of (not only) IoT-powered healthcare mobile apps?
- Engaging healthcare mobile apps have simplified and facilitated interactions with doctors, resulting in increased patient satisfaction and engagement.
- Such apps allow for remote monitoring of a patient’s health that can reduce hospitalizations and readmissions by reducing the length of their stay. Constant tracking of health conditions keeps family members and health providers informed of a person’s changes and disturbances.
- By reducing healthcare costs and improving outcomes, these services can make a significant difference to the healthcare industry.
- The connected wearables introduce routine into daily activities in healthcare, notifying users about calorie counts, exercise checks, appointments, or blood pressure levels.
- The use of healthcare apps can help physicians measure patients’ adherence to treatment plans and determine whether patients need immediate medical attention, as well as the use of IoT devices to identify the best way to treat them.
- Sensor-filled IoT devices are used for tracking medical equipment’s location, monitoring equipment’s performance, and dispatching medical staff in real-time, as well as taking care of asset management and preventing patients from getting infected due to the monitoring.
- Transparency in shared data between insurers and customers is enabled by IoT healthcare mobile apps in terms of pricing, handling claims, and risk assessment.
Benefits of Gamification in Healthcare Apps
Gamification in healthcare apps transforms health management into an engaging experience, leveraging game mechanics to motivate and educate users.
Boosting Engagement in Health Apps
By incorporating gamification elements, tracking health becomes more than routine; it’s an engaging part of daily life, significantly enhancing health outcomes.
Ensuring Treatment Adherence in Gamified Healthcare Apps
Gamification strategies in apps like Mango Health motivate users to adhere to their health plans, crucially improving patient outcomes.
Promoting Health Knowledge for Wellness
Utilizing the concept of gamification, educational content becomes an entertaining tool for learning about digital health, making complex information more accessible.
Building Community Support Through a Healthcare Game
Social features within health apps create a supportive network, helping users achieve their health goals and fostering a sense of accountability.
Delivering Tailored Feedback in Health Apps
Immediate, personalized feedback guides users in adjusting their health strategies effectively, showcasing how gamification can be used in the healthcare industry to support wellness and improve patient engagement.
This approach aligns with current healthcare trends, illustrating how gamification in healthcare apps not only entertains but also serves to help healthcare providers engage and educate their patients more effectively.
How to Develop and Connect an IoT Device to a Mobile App? – Examples in Healthcare
The IoT itself contains a few subsequent steps, each representing a specific stage of a process. Each stage collects or processes data that will be used by the other stages.
It first consists of deploying interconnected devices such as sensors, monitors, or cameras so that the data can be collected. For performing the next step, it is necessary to aggregate analog data from sensors and other devices into a digital format. Then, upon digitization, standardization, and aggregation, the data is transported either to a data center or cloud. Applied advanced analytics to final data provides actionable business insights that facilitate making the right decisions.
It is imperative that such apps have a well-planned communication protocol, security, and encryption. How can some sample security features be described? If you’ve already paired the first device, you’ll be unable to connect the second. As an example, the system might generate a dedicated key for the app and for the device. A great deal of sensitive data is stored in healthcare applications, so privacy is extremely important.
The healthcare mobile apps are compatible with Bluetooth, WIFI, and NFC. Bluetooth ranks number one among all these methods, but let’s spend a brief moment analyzing all of them.
Bluetooth
Because Bluetooth allows devices to connect directly, it has been the most popular method for connecting apps to devices and devices with each other without the use of the network. Typically, healthcare mobile apps are connected directly to a particular device. By combining proximity technology from NFC with a strong wireless signal, Bluetooth offers the best of both worlds.
Also, such devices can connect to the Internet indirectly, using an external service, and only then sending information to users.
Other devices can connect to users through a connection to some other device. Sensors like anti-theft ones work in this manner. They connect to databases, and then through an external server, to users and devices.
In addition, there is the direct connection model that utilizes a SIM card. In this way, the device communicates with the servers and the backend of the system over the Internet. Data processing is optimized on the servers.
NFC
The range and signal of NFC are very limited. As we are only talking about a few centimeters here, it would be sufficient to open locks with cards, pay with a card, or send documents to a printer.
WiFi
WiFi is rare and it would be more beneficial for one-to-one devices. Connecting devices over the network, instead of directly, is possible with WiFi. All transmissions are handled by an external server. We can differentiate two types here:
- Device-to-device via WiFi: usually plays a role of an introduction to a much more advanced configuration or integration with other technologies,
- device-to-network: for example, to a network printer.
A number of IoT devices do leverage direct connections due to their specifics, e.g. smartwatches or various in-car devices.
There’s also one more tweak to take into account – Bluetooth low energy. In this regard, preparing the system for a variety of scenarios is advisable. First of all, the battery consumption should always be monitored by the system. When it needs to be charged, it should provide notifications so that the device can last longer, be protected from failure, and always be charged and ready to use. Secondly, the system’s consumption needs to be optimized to the maximum.
How to use IoT in healthcare mobile apps
In addition to its many benefits, gamification focuses and drives users’ attention, taps into innate abilities, excites users utterly, and strengthens the ability to achieve more powerful outcomes. In healthcare, this creates a fertile ground for behavior change.
Playing a game means more than just collecting vitals and getting notifications, as gamified healthcare mobile apps can keep users engaged and truly motivated. If we also consider that downloading and using the apps is voluntary, healthcare mobile apps could help achieve great things in healthcare and revolutionize the field.
Health advice, video chat, and video appointments with doctors and receiving prescriptions and self-tracking health are all now available via smartphones, and its growth was facilitated by the pandemic outbreak.
In the following sections, you can read about healthcare mobile apps that motivate, reward, and reinforce commitment, as well as IoT solutions.
PelviFly
Using a device and a mobile application, PelviFly allows safe and effective pelvic floor muscle training. Women of all ages can train pelvic floor muscles through PelviFly, which integrates a gaming experience with medical treatment.
We at CrustLab were a part of the process of reengineering this mobile app.
You can read more on it here.
PelviFly operates in the healthcare market in Mid and West Europe. PelviFly has a small team of coaches and specially trained medical and physiotherapists working with it. Their efforts have resulted in more than 20,000 women regularly training their pelvic floor muscles with PelviFly’s product.
Women exercising with PelviFly can be kept informed during training sessions about the progress or abnormalities. It is possible for the coach to send these notifications as well. Additional coaching could also be purchased and paid for with an attached bank card.
FitBit
Fitness tracking app FitBit is a popular app that supports healthy lifestyles worldwide.
Using FitBit, users can create challenges on the FitBit community interface and compete to see who gets better results at the gym and who does more steps.
You can track any running, cycling, or other workouts with SmartTrack on Fitbit’s multi-sport mode. Each type of exercise is recorded using a different algorithm, providing the most accurate evaluation of your performance. In addition to the number of steps, it can also measure other activity parameters with great precision; and with the integrated GPS, it even has even more data.
All of this is connected to a mobile app, of course. To ensure the best results, Fitbit’s mobile app connects to the Fitbit wristwatch. As you’ll see in the next examples, a marriage between wearable technology and mobile apps is not new or revolutionary, though!
Bayer’s Didget
Didget, made by Bayer and compatible with Nintendo DS gaming systems, is a blood glucose meter that connects to kids ages 4 to 14. By rewarding them for consistently testing their blood glucose levels, it helps manage their diabetes. Furthermore, it promotes setting up treatment goals tailored specifically to each child’s needs. Two levels of testing allow for growth as children become more capable of managing their diabetes. A new level and option become available as the player accumulates points. Leaderboards showing top points collectors, web games, and an online community are also available.
Huawei Body Fat Scale
Scale 3 is an intelligent bathroom scale that can measure 11 body composition indicators at once.
With its Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity, the Huawei scale can be easily connected to your smartphone and controlled using the Huawei Body Fat Scale app. App users can view, among other things, their body weight, muscle weight, basal metabolic rate, or water content in their bodies. In addition, the app displays trends, provides advice, and allows access to the results history. As you want to improve your results on a daily basis, this reinforces internal gamification with your own body.
MySugr
mySugr, a startup based in Austria, offers fun digital solutions for diabetics. The app is suitable both for children (mySugr Junior) and adults.
More than a million users have already signed up for MySugr, which is available in 52 countries and 13 different languages.
MySugr lets patients track the blood sugar, carbs, bolus, and estimated HbA1c of their own body with one glance. The users of this app have been able to better control their condition since they log their data each day. The data is also available to physicians so they can provide better and more customized treatment.
Using this app, users can also receive real-time feedback for dealing with diabetes Type 1 or Type 2. Having diabetes is difficult, and this app has made life a bit easier.
Healthcare Gamification Market – Can a Healthcare App Replace Regular Appointments?
With the goal of delivering ease and convenience, healthcare providers are working tirelessly to transform their mobile app development services. Mobile healthcare apps are set to continue being an exciting development field. Despite their imperfections, these apps provide users with care when and where they need it.
Patients are also still encouraged to attend checkups in person if necessary because apps cannot fully replace in-person appointments. As we have seen with the pandemic, though, unexpected events are capable of quickly proving the relevance of technologies.
Many people have benefited from these apps, so it’s not just another trend, it’s a real trend that will probably change lives for the better.

